Navigating the complication of chargebacks can be intimidating, time-consuming, and expensive. While all parties involved bear some cost, businesses often bear the major brunt of the financial burden.
Given these challenges, is it worth contesting chargebacks? If so, how can online businesses effectively dispute them?
In this guide, we’ll simplify the chargeback resolution process, highlighting potential pitfalls and strategies to address them for Online Payments and how Merchants in Qatar can handle the Chargebacks more effectively.
What is the Chargeback Process?
A chargeback occurs when a credit card holder disputes a transaction and seeks resolution from their issuing bank. This process can involve multiple stakeholders, including issuers, acquirers, merchants, vendors, card networks, and crucially, payment gateway service providers.
At its core, the chargeback mechanism offers a safety net for consumers: if a resolution can’t be reached with the merchant, the bank steps in. However, the actual process is intricate, with numerous steps to navigate. The diagram below provides a simplified overview: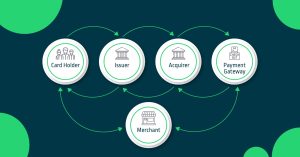
Key Players in the Chargeback Process:
Cardholder: The individual who owns the card used in the transaction.
Merchant: The entity selling the disputed goods or services.
Card Issuer Bank: The financial institution that issued the card to the holder i.e Qatar Islamic Bank, Doha bank, Commercial Bank etc.
Acquirer Bank: The bank responsible for processing payments on behalf of the merchant i.e Doha Bank, Qatar National Bank etc.
Payment Gateway: A crucial intermediary that facilitates the transaction between the merchant and the acquiring bank. They play a pivotal role in helping both parties prepare their case in the event of a chargeback, acting as a liaison to ensure smooth communication and process flow. ie. TESS Payments, and others PSP’s of Qatar.
Card Network: The card brands (e.g., Visa, Mastercard, NAPS etc) that oversee the entire process.
Chargeback Process: Step-by-Step
Throughout the chargeback process, various challenges can arise, complicating resolution. Here’s a detailed breakdown:
STEP #1: Dispute Initiation
The process commences when a cardholder informs their bank of a transaction issue. Each distinct issue can trigger a separate chargeback.
STEP #2: Provisional Refund
Initially, the cardholder receives a conditional refund. Subsequently, the bank retrieves the funds from the merchant’s payment processor, which then deducts the amount from the merchant’s account.
STEP #3: Assigning a Reason Code
The issuing bank assigns a code detailing the chargeback’s cause. This information, along with other relevant details, is electronically forwarded to the merchant’s payment processor or acquirer.
STEP #4: Re-Presentation Option
Merchants can either accept the chargeback or contest it. The Chargeback Debit Advice letter from the acquirer provides insights to guide this decision.
STEP #5: Document Compilation
Merchants must promptly gather all necessary documentation to challenge the chargeback, including evidence supporting their stance. The payment gateway can assist in collating and presenting this information effectively.
STEP #6: Representment Package Submission
The merchant’s response and evidence are sent to the payment processor or acquirer, which then forwards it to the issuing bank.
STEP #7: Bank Review & Outcome
The issuer evaluates the provided information, leading to one of three potential outcomes:
Merchant’s victory: The initial transaction is validated, and funds are returned to the merchant.
Cardholder’s victory: The bank remains unconvinced, and the chargeback stands.
Secondary chargeback: The issuer can file another chargeback for the same transaction, typically due to new evidence or a changed reason code.
STEP #8: Arbitration
In this critical phase, the card network (e.g., Visa, Mastercard) is called upon to deliver a final verdict. The losing party may incur significant penalties.
Potential Chargeback Complications
The chargeback process, while designed to protect consumers, has its flaws:
Subjectivity: The outcome often hinges on individual interpretations of rules and guidelines.
Outdated Framework: The chargeback system predates the digital age, making it ill-suited for contemporary challenges.
Bias Towards Consumers: Banks typically side with their customers, inadvertently encouraging misuse.
Fraud Potential: Malicious actors can exploit the system for illicit gains.
Inequity: Smaller businesses might lack the resources to contest chargebacks, viewing them as an unavoidable expense.
While these challenges might seem daunting for merchants, knowledge is power. By understanding the intricacies of the chargeback process, businesses can better navigate and address potential pitfalls.


